Security researchers from Microsoft have developed the Whisper Leak side-channel attack technique, allowsto classify the topics of requests to services based on large language models based on passive analysis of encrypted traffic transmitted over a TLS connection. Information about the size of network packets and delays between their transmission was sufficient to determine the topics of requests to AI chatbots with an accuracy of more than 98%. In practice, the proposed method can be used to identify certain query topics in the user’s transit traffic, for example, attempts to obtain information about illegal actions, without decrypting the content.
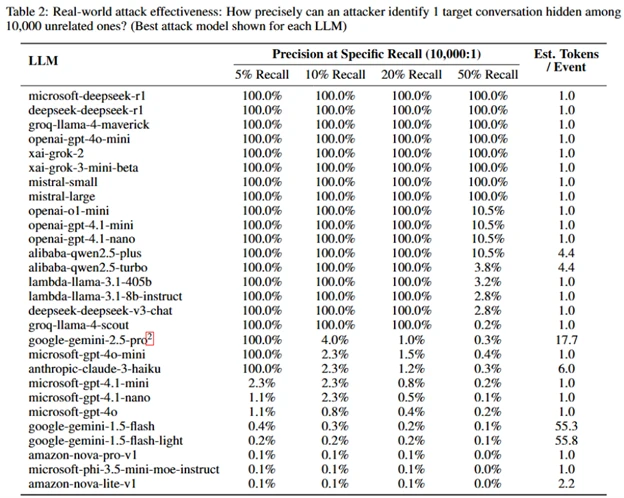
Toolkit for extracting data from traffic dumps, training the model and testing the operation of the method published on GitHub. The attack has been demonstrated for 28 popular large language models from major vendors. For example, the accuracy of identifying requests on the topic “money laundering” for many AI services was 100%, when the analyzed traffic contained 1 desired request and 10,000 requests not related to the desired topic.
The reason for the information leak is that the models generate a response to the request step by step, one by one token at a time, at each step using the previous token as context to determine the next most likely word or phrase. Accordingly, a separate network packet is sent for each token, and the delay between packets corresponds to the delay between the model determining the next token.
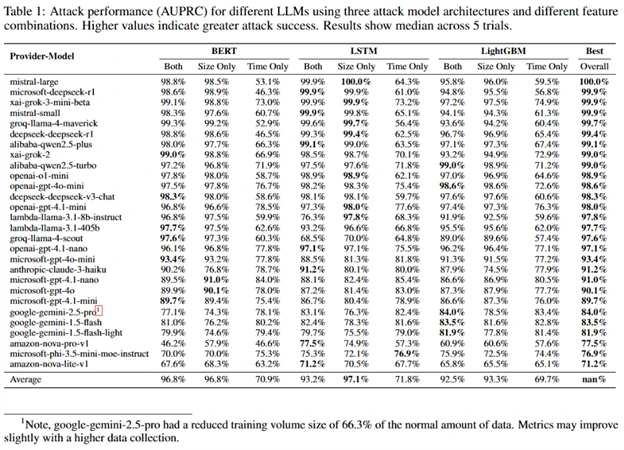
In TLS, if data compression is not used, the ciphertext exchange is equal to the size of the plaintext plus a constant. By creating a model that compares the required sets of tokens with the size of the packets and the delays between their sending, it is possible to fairly accurately determine the presence of the desired topics in the traffic. During the study, three versions of such machine learning models were prepared, based on the LightGBM, Bi-LSTM and BERT neural network architectures. For each model, experiments were conducted to determine the desired topic by analyzing only the size of packets, only delays between packets, and both criteria.
To reduce the effectiveness of passive query subject analysis, AI service developers are encouraged to attach random padding, buffer token transfers, or perform dummy packet substitution.