Researchers from CodeRabbit analyzed 470 pull requests (350 created by AI, 150 written by hand) in open projects on GitHub and came to the conclusion that changes generated by AI assistants contain 1.7 times more significant defects and 1.4 times more critical problems than in manually written code. On average, AI-generated pull requests had 10.83 issues, compared to 6.45 issues in manually generated changes.
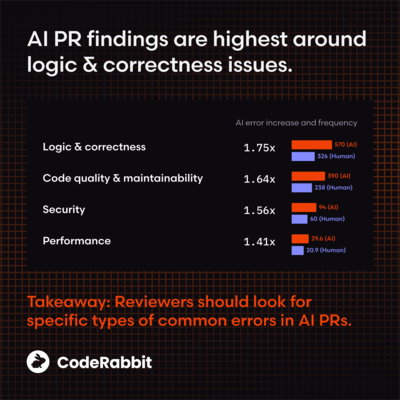
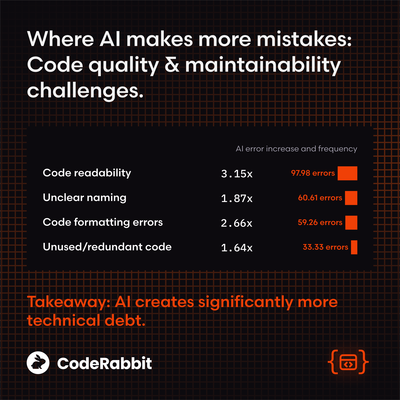
When looking at individual issue categories, AI-generated code had 1.75 times more logic errors, 1.64 times more code quality and maintainability issues, 1.56 times more security issues, and 1.41 times more performance issues. Additionally, it is noted that in code generated through AI, the likelihood of incorrect password processing is 1.88 times higher, the likelihood of insecure provision of access to objects is 1.91 times higher, cross-site scripting (XSS) is 2.74 times higher, and insecure data deserialization is 1.82 times higher. At the same time, human-written code has 1.76 times more spelling errors and 1.32 times more testing-related errors.

Some other studies:
- In a studyconducted in November by Cortex noted that, compared to last year, the use of AI increased the average number of pull requests created per developer by 20%, but the number of issues in pull requests increased by 23.5%, and Change failure rates have increased by approximately 30%.
- An August study from the University of Naples concluded that AI-generated code is generally simpler and more consistent, but contains more unused constructs and built-in debugging inserts, while hand-written code is structurally more complex and contains more maintainability problems.
- The July experiment of the METR group showed that AI assistants do not speed up, but slow down the solution of tasks, despite the fact that subjectively the participants believed that AI sped up their work.
- A January study from Monash University found that GPT-4 generates more complex code that requires further maintenance, but does a better job of passing tests.