Researchers from the Ben-Gurion University (Israel) studying the hidden methods of transferring data from isolated computers developed a new method of organizing a communication channel – AIR-FI, which allows, through manipulation of DDR memory chips, to generate a radio signal at a frequency of 2.4 GHz, which can be caught by any device with Wi-Fi support at a distance of several meters. From a practical point of view, the method can be used to transfer encryption keys, passwords and secret data from a computer that does not have a network connection and is infected with spyware or malware.
Researchers managed to achieve a transfer rate of 100 bits per second when placing Wi-Fi receivers, such as a smartphone or laptop, at a distance of 180 cm. The transmission error rate was
8.75%, but error correction codes were used to identify and correct transmission failures. To organize a data transfer channel, it is enough to launch a normal user process, which can also be executed in a virtual machine.

DDR4 memory ability was used during signal generation 2400 generate electromagnetic interference at a frequency of 2400 MHz when the controller accesses the memory module over different data buses. The Wi-Fi range falls on the frequencies 2.400-2.490 GHz, i.e. radically different. However, the researchers found that overlapping signals from different data buses could emit 2.44 Ghz electromagnetic waves captured by the 802.11 wireless stack. To generate a signal, a simultaneous access to the bus was used from parallel executed threads tied to different CPU cores.
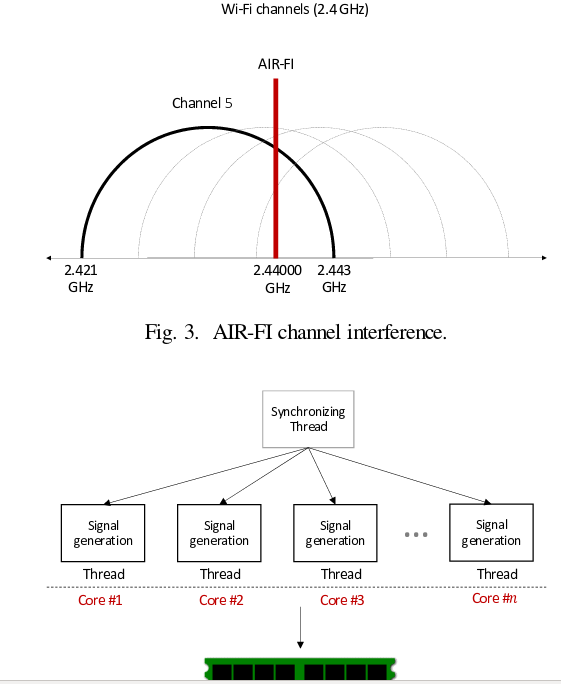
To encode useful information in the signal, we used the simplest OOK modulation (on-off keying) with amplitude shift keying (ASK), with which “0” and “1” are encoded by setting different signal amplitudes, and information is transmitted at a fixed rate – one bit per millisecond. Transfer “1” performs a series of memory writes caused by sequential copying of 1 MB of data between the two arrays. When transmitting “0”, the algorithm does not perform any action for the time allotted for transmitting a bit. Thus, transmitting “1” generates a signal emission, while transmitting “0”, the signal disappears.
Among the measures to counter the use of the AIR-FI method, zoning of the territory is mentioned with the creation of a perimeter in the organization, into which it is prohibited to carry equipment with wireless chips, as well as placing a computer case in a Faraday cage, generating noise at Wi-Fi frequencies, starting background processes that perform random memory operations, and monitoring the appearance of suspicious processes in the system that perform abnormal memory operations.